Tất cả
Hỏi bài tập Toán Học
Vật Lý
Hóa Học
Tiếng Anh
Ngữ Văn
Hỏi đời sống Tâm lý cảm xúc
Tình cảm
Gia đình bạn bè
Cơ thể & Dậy thì
Giải trí
Mạng xã hội
Định hướng cuộc sống
Hỏi đáp ẩn danh
hhhhhhhhjjjjjjjjjj

 0
0
-
Câu trả lời phải chính xác, đầy đủ dựa trên kiến thức xác thực:
- ✔ Đối với câu hỏi trắc nghiệm: Đưa đáp án lựa chọn + giải thích lý do chọn đáp án.
- ✔ Đối với câu hỏi tự luận: Đưa lời giải và đáp án cho câu hỏi.
- ✔ Đối với câu hỏi trả lời ngắn: Đưa ra đáp án + giải thích lý do.
- ✔ Chấp nhận sử dụng ảnh do thành viên viết tay, ảnh cần rõ nét, không bị mờ, vỡ ảnh.
- Sử dụng ngôn ngữ rõ ràng, dễ hiểu.
- Tránh đưa ra các ý kiến cá nhân mang tính chất chủ quan.
- Nếu sử dụng thông tin từ nguồn khác, phải trích dẫn nguồn đầy đủ và chính xác.
- Tuyệt đối không được sao chép các thông tin từ các trang khác, từ AI hoặc chatGPT.



02/03/2025
 0
0
02/03/2025
Bài 4:
1) Xét $\displaystyle \vartriangle ABC$ vuông tại A có:
$\displaystyle AB=AC.tan\widehat{ACB} =1.tan30^{0} =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3} \approx 0,6( m)$
Vậy cây tre cao khoảng 0,6m
2)
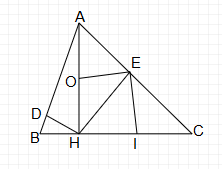
a, Ta có: $\displaystyle \widehat{AEH} =\widehat{ADH} =90^{0}$
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow D,E$ thuộc đường tròn đường kính AH
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow A,E,D,H$ cùng thuộc 1 đường tròn tâm O là trung điểm của AH
b, Xét $\displaystyle \vartriangle AHB$ vuông tại H có: HD là đường cao
Theo hệ thức lượng ta có: $\displaystyle AH^{2} =AD.AB$ (1)
Xét $\displaystyle \vartriangle AHC$ vuông tại H có: HE là đường cao
Theo hệ thức lượng ta có: $\displaystyle AH^{2} =AE.AC$ (2)
Từ (1) và (2) ta có: $\displaystyle AD.AB=AE.AC$
c, Ta có: $\displaystyle \begin{cases}
\widehat{HAC} +\widehat{ACH} =90^{0} & \\
\widehat{HAC} +\widehat{AHE} =90^{0} &
\end{cases} \Longrightarrow \widehat{ACH} =\widehat{AHE}$
$\displaystyle \vartriangle AHE$ vuông tại E có: EO là đường trung tuyến ứng với cạnh huyền
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow EO=\frac{AH}{2} =HO\Longrightarrow \vartriangle OEH$ cân tại O$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow \widehat{AHE} =\widehat{OEH}$
Do đó $\displaystyle \widehat{ACH} =\widehat{OEH}$
$\displaystyle \vartriangle HEC$ vuông tại E có: EI là đường trung tuyến ứng với cạnh huyền
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow EI=\frac{HC}{2} =HI\Longrightarrow \vartriangle HEI$ cân tại I
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow \widehat{IEH} =\widehat{CHE}$
Ta có: $\displaystyle \widehat{EHC} +\widehat{ECH} =90^{0} \Longrightarrow \widehat{OEH} +\widehat{IEH} =90^{0}$
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow \widehat{IEO} =90^{0} \Longrightarrow EI\bot OE$
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow $IE là tiếp tuyến của (O)
Bài 5:
$\displaystyle \begin{array}{{>{\displaystyle}l}}
7x^{2} +y^{2} +4xy-24x-6y+21=0\\
\Longrightarrow 4x^{2} +4xy+y^{2} -12x-6y+9+3x^{2} -12x+12=0\\
\Longrightarrow ( 2x+y)^{2} -2.( 2x+y) .3+9+3\left( x^{2} -4x+4\right) =0\\
\Longrightarrow ( 2x+y-3)^{2} +3( x-2)^{2} =0
\end{array}$
Với mọi x,y ta có: $\displaystyle \begin{cases}
( 2x+y-3)^{2} \geqslant 0 & \\
( x-2)^{2} \geqslant 0 &
\end{cases}$
$\displaystyle \Longrightarrow ( 2x+y-3)^{2} +3( x-2)^{2} \geqslant 0$
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi và chỉ khi:
$\displaystyle \begin{cases}
2x+y-3=0 & \\
x-2=0 &
\end{cases} \Longrightarrow \begin{cases}
x=2 & \\
y=-1 &
\end{cases}$
 0
0
Nếu bạn muốn hỏi bài tập
Các câu hỏi của bạn luôn được giải đáp dưới 10 phút
CÂU HỎI LIÊN QUAN
31/08/2025
31/08/2025
31/08/2025
31/08/2025
Top thành viên trả lời







